Gums–Periodontal Health
Periodontics is the treatment of gum disease that impacts the gums and bones surrounding the teeth. Fortunately, periodontal disease can be prevented by maintaining good oral hygiene.
What Sets us Apart to other Practices
Maintaining Oral Hygiene
It is essential to look after your teeth and remove the buildup of plaque. Here are some simple tips that can help in keeping a healthy mouth:
- Brush your teeth – Two minutes twice a day. Do not brush too hard as it can damage your gums .
- Floss daily – This helps remove food particles that are stuck in between teeth, and below the gum line, which cannot be reached using a toothbrush.
- Always use fluoride toothpaste – makes teeth stronger and helps counteract harmful acid from food & drink.
- Visit your dentist – twice a year for your regular check-up.
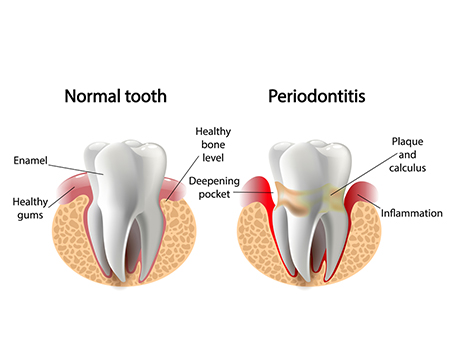
Healthy Gums
Some common signs in identifying healthy gums:
- Gums should be firm and pink.
- Healthy teeth and gums should not bleed while brushing or flossing.
- Pleasant smelling or neutral breath.
- There should not be any inflammation or redness of the gums.
If you do not keep your mouth healthy and remove the plaque every day, the build-up will lead to gum disease like Gingivitis.
What is Gingivitis?
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gum caused by a bacterial infection due to the buildup of plaque. Without regular brushing and flossing, the plaque increases by feeding on sugar found in drinks and food that sticks in your mouth.
If left untreated, gingivitis can lead to severe periodontal disease.
Symptoms of Gingivitis:
- Gums are sore, swollen, puffy and red.
- Gums bleed during brushing or flossing.
- Discomfort and pain
- Loose teeth
- Bad smelling breath.
What is Periodontal Disease?
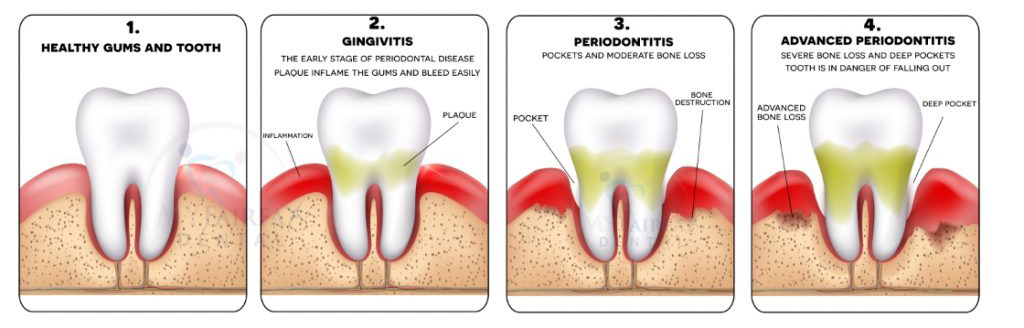
The later stage of gum disease is known as Periodontal Disease. The bacterial infection progresses deeper and damages the soft tissue and bone supporting the tooth. Teeth are no longer anchored in place; they become loose and leads to tooth loss.
Periodontal disease is irreversible, but treating the infection will slow down the progression.
Various treatments can be taken:
- Scaling and root planning: this involves deep cleaning of teeth and root surfaces.
- Bone grafts: adding bone tissue, to create a platform for regrowth and strength.
- Soft Tissue Grafts: tissue is taken from your palate and uses seals to place this where your gum is in recession.
- Prescription medication: the option to prescribe antibiotics, antifungals, and gels that help treat and stop the progress of the disease.
- Gum recontouring: If the recession of your gums ends up giving you a “toothy” smile, your dentist can re-contour the gingival tissue. The procedure will correct and even out your smile.
It is hence vital that you take care of your oral health and visit your dentist regularly to see if you have any oral issues that can be prevented before it becomes severe.
“There is always a risk for any surgical or invasive procedure. Hence, before proceeding, we recommend you to seek a second opinion from an appropriately qualified health practitioner.”









